- A case report of a patient presented with skin ulcer after treatment of lenvatinib
-
Serin Cha, Dong Woo Kim, Jung Wan Choe, Tae Hyung Kim, Seung Young Kim, Jong Jin Hyun, Sung Woo Jung, Ja Seol Koo, Young Kul Jung, Hyung Joon Yim
-
J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(2):194-198. Published online September 30, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2021.09.20
-
-
3,312
Views
-
78
Downloads
-
1
Citation
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
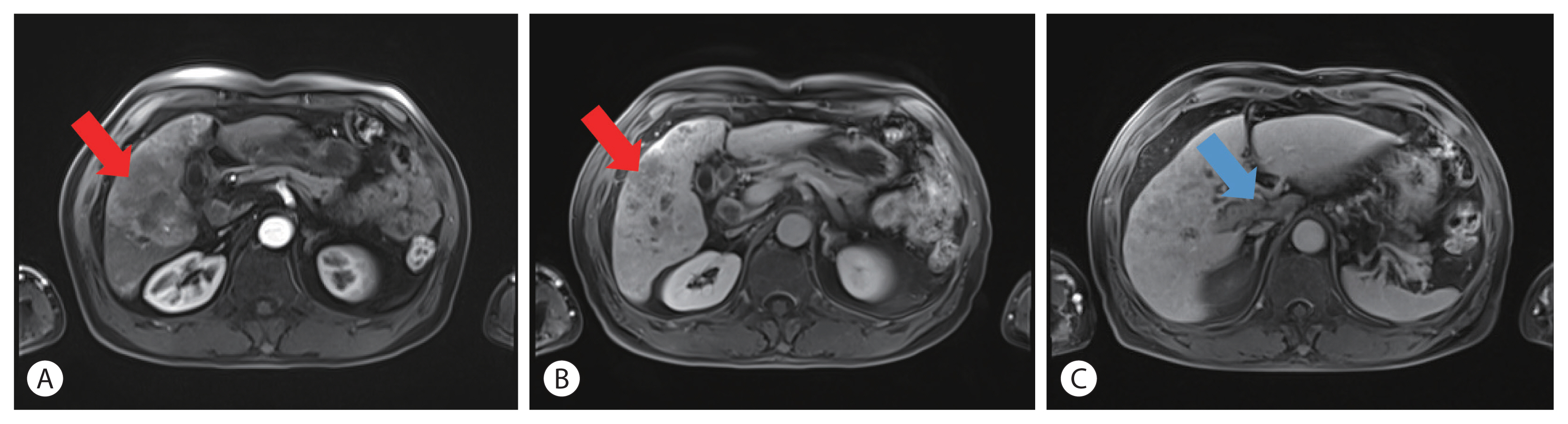
- A 60-year-old man diagnosed with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presented to the hospital with pain in the perineal region. He had been taking lenvatinib every day for 2 months after he was diagnosed with HCC with metastases to the lymph node, small bowel mesentery, and retroperitoneal space. Enhanced abdominal computed tomography revealed mild elevation in intensity in the perineal subcutaneous tissue with subcutaneous emphysema. The patient was diagnosed with Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events grade 3, skin ulceration of stage IV with full-thickness skin loss and tissue necrosis in the muscular layer. The patient was taken off the medication with prescription of antibiotics, and after 3 weeks, the skin has fully recovered. This is the first report of an HCC patient who presented with a skin ulceration of stage IV after lenvatinib treatment. We recommend stopping the medication immediately and changing to alternative treatments with appropriate supportive care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Multiple lenvatinib‐associated skin ulcers: A case report and literature review
Soo Hyun Jeon, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Sung Eun Chang, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung
Australasian Journal of Dermatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Case of Simultaneous Resection of Recurrent Combined Hepatocellular Cholangiocarcinoma and Hypovascular Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Tae Hyung Kim, Soon Ho Um, Sang Jung Park, Seung Woon Park, Han Ah Lee, Yeon Seok Seo, Young Dong Yu, Dong-Sik Kim, Joo Young Kim
-
J Liver Cancer. 2017;17(1):94-99. Published online March 31, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.17.1.94
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Liver cancer is more complex to treat compared to cancers in other organs, since liver function
should be considered. In addition, only a few patients can be applied curative treatment due to
advanced stage at diagnosis. Therefore, early stage detection is important and has been increased
through screening and surveillance programs using image modalities recently. However, it is still
difficult to diagnose small or hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) even using advanced
image modalties. In particular, hypovascular HCCs do not show arterial contrast enhancement
which is a typical finding of HCC on computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI). Those also account for a considerable portion of early HCC. We present 54 yearsold
man who had recurrent hypervascular and hypovascular nodules on three phase CT and
gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. The nodules were removed by surgical resection and confirmed
as combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and well differentiated HCC respectively.
- A Case of Management for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Lung Metastasis
-
Han Jo Jeon, Tae Hyung Kim, Soon Ho Um, Yeon Seok Seo, Hyun Seo Kim, Ki Joon Lim, Seung Woon Park, Han Ah Lee, Dong-Sik Kim
-
J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(2):129-133. Published online September 30, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.2.129
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Liver cancer is the 2nd most common cause of cancer related death in Korea. Especially,
patients who present extrahepatic spread of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have a shorter life
expectancy (50% survival at 1 year and less than 4 months of median overall survival). Molecular
target agent like sorafenib was usually mentioned as a treatment for them, but that was still not
firmly established. We present a 75 year-old who had expanding nodular type of HCC. The mass
was removed by resection and radiofrequency ablation. However, lung metastasis were revealed
shortly after surgery. That lesions were treated with lenvatinib and systemic chemotherapy.
- Clinical Outcome of Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Single Session in Patients with Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis
-
Min Seon Park, Soon Ho Um, Ho Sang Ryu, Yeon Seok Seo, Sun Young Yim, Chang Ho Jung, Tae Hyung Kim, Dae Hoe Gu
-
J Liver Cancer. 2014;14(2):139-142. Published online September 30, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.14.2.139
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Most cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) occur in the Asia-Pacific region and in patients
with underlying hepatitis B and C viral infection. Although surgical resection is the gold
standard for treatment of HCC, only a few patients are surgical candidates because of their
lack of hepatic reserve. Liver transplantation, which eradicates HCC and replaces damaged
noncancerous hepatic parenchyma, is regarded as the best treatment for HCC in patients
with decompensated liver cirrhosis. However, the shortage of donors limit its widespread
use. Furthermore, the long waiting time for liver transplantation allow for tumor progression
and reduce patient survival. Given this long wait, there is a reasonable clinical need in the
meantime for minimally invasive methods to avoid progression of HCC in patients with
decompensated liver cirrhosis. We herein offer our experiences of therapeutic efficacy and
complications of the procedure and the changes in liver function before and after TACE and
radiofrequency ablation in patients with HCC and decompensated liver cirrhosis, defined as a
Child-Pugh-Turcotte score above 7. (J Liver Cancer 2014;14:139-142)
|